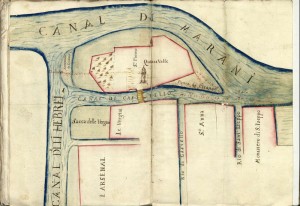
האזור הוגדר על ידי שני שערים אשר, כפי שציין ידי הסנאט ב -29 במרץ, 1516, ייפתחו בבוקר לקול של "Marangona" (הפעמון במגדל הפעמונים של סן מרקו שכונן את לוח הזמנים היומי של העיר) וסגר בלילה בחצות ידי ארבעה שומרי נוצרי, שמשלם היהודים ודרש להתגורר באתר ללא משפחתם כדי להיות מסוגל יותר למלא את חובותיו הפיקוח שלהם. יתר על כן, שני קירות גבוהים היו נבנו (אבל אף פעם לא נבנו) כדי להקיף את האזור בצד של תעלות המקיפות אותה, דפון את כל הבנקים על אמר תעלה. שתי מועצת עשר סירות עם שומרים שמשלמים "שוכני הטירה" החדשים שייט לאורך התעלה ברחבי האי בלילה כדי להבטיח את ביטחונה.
לפי השאלות הבאות -1 באפריל, "grida" ( "ההצהרה") הוכרז ריאלטו ומן הגשרים בכל מחוז עיר שבה התגוררו יהודים.מאורגן לרגל שנת המאה החמישית של יצירת הגטו של ונציה, שאצרה דונטלה Calabi עם התיאום המדעי של גבריאלה Belli והתרומה של מאגר גדול של חוקרים, ונציה, היהודים ואירופה 1516 - 2016 תערוכה שואפת לתאר התהליכים שהביאו ליצירת וליווי השינוי של "גדר" הראשון עבור היהודים בעולם.
במקביל, התערוכה מתרחבת אופק רחב יותר, מחבק את הקשרים שנוצרו עם שאר חלקי העיר ועם היהודיות אחרים (ואחרים) מחוזות באיטליה ובאירופה, כדי להדגיש את היחסים הפורים בין יהודיי וונציה ובין היהודים חברה אזרחית בתקופות השונות של השהות הארוכה שלהם בלגונה, באזור ונטה באירופה ובארצות הים התיכונה. הכוונה היא להקים מודעות גדולות יותר של ההווה המגוון התרבותי בוונציה קוסמופוליטית בתחילת המאה שש עשר והתמהיל של ידע, מיומנויות, מנהגים שעדיין מהווים המורשת החשובה ביותר שלה.
יש משימת תערוכת veniceThe ובכך לא הייתה רק אחד מדידות באזור המיוחד של השלושה גטאות (נואובו, וקיו Nuovissimo), אלא גם אחד השתקפות בבורסות התרבותיות ולשוניות, את אומנות הקנס ונסחרת שהקהילה היהודיה שתפה האוכלוסייה הנוצרית ומיעוטים אחרים, המתגוררים בעיר מרכנתיל חשוב מאוד שלפנינו. משך הזמן הנחשב חורג נפילת הרפובליקה ופתיחת הדלתות לבקשתו של נפוליאון: התערוכה גם להציג את תפקידם של יהודים בעידן של התבוללות במהלך המאה עשרים.
ציורים חשובים - על ידי בליני קרפצ'יו, Foraboschi, Hayez ו Poletti, Balla ו וילט כדי שאגאל - שרטוטים אדריכליים של התקופה, כרכים במהדורות מקוריות נדירות מאוד, מסמכים ארכיוניים, חפצי פולחן וריהוט, יחד עם שחזורי מולטימדיה ייאפשרו את המבקר ללמוד על מערכת יחסים ארוכת טווח כי היה מסומן גם על ידי חדירות, קשרים הדוקים וחילופי תרבות.
ההנחה הראשונית של הפרויקט גורסת כי ההיסטוריה של המוסד בגטו בוונציה צריכה להילמד במסגרת התמונה הכללית יותר של הממשל של וונציה הרפובליקה של מיעוטים לאומיים, אתניים ודתיים המתגוררים בעיר, בירתה של "כלכלה עולמית" , כפי שמציין ההיסטוריון פרנאן ברודל קרא לזה. אבל זה גם מתיימר להסביר כיצד יחסים אלה התרחבו בהדרגה לאזור גיאוגרפי הרבה גדול הרבה התמידו לאורך זמן, הסתגלות לשינויים פוליטיים, חברתיים ותרבותיים.
בעשורים הראשונים של המאה השש עשרה הרפובליקה של ונציה יישמה אסטרטגיה מכוונת של מוזמנים, בו זמנית מציע ערבויות ומעקב, שהיה פחות או יותר נוקשה ביחס קהילות לאומיות ודתיות שונות; בברכה זו הוארך לקהילות שהיו חשובים לפעילות הכלכלית של הרפובליקה, כגון צפון אירופאים (עם טדסקי Fondaco dei), היוונים האורתודוקסים (עם ויתור לבנות כנסייה מכללה על חשבונם), ובמשך שנים, אלבנים, פרסים וטורקיים.
היהודים, כמו מיעוטים האחרים, היו "יקרים" עבור סרניסימה (כפי שאנו קוראים מסמכים מסוימים): שופטת, כמה מהנתונים אצילים, הדוג'ה לאונרדו לורדאן עצמו, שהיה "נסיך" בעת גזירת קום (29 במרץ , 1516), היו מודעים היטב לכך. אף על פי כן, ונציה, אשר אפשרה ליהודים בשטחן להיכנס לעיר כפליטי מלחמה - ב בשלב כשאירופה הייתה לגרשם מספרד (1492) ופורטוגל (1496) - בעקבות ההשלכות הדרמטיות של הליגה של Cambrai ותבוסת Agnadello, בקרוב הנשקף עצמו בשאלה כיצד להתייחס למיעוט היהודי.
"על כף המאזניים היה הגנה על ערכי היסוד של תרבות עבור על התפיסה העצמית. כלומר ", על פי ראובן בונפיל," כל אותם ערכים כי "המיתוס של ונציה" יראוהו החיוניים ביותר של כל: צדק, חופש ושגשוג, כל מושרשת ממשל תקין ולא לפחות בהגנה על האתיקה הנוצרית, שבלעדיו לא צדק ולא שגשוג היה דעת ".
ההחלטה שלא לגרש את היהודים אלא לשמור אותם בתוך הגטו נתפס הרע במיעוטו המתחם שלהם, כשלעצמה פלייה גלויה, בסופו של דבר ייפול גם הגנה טובה, משום שהיהודים, ישות חלשה פוליטי מחוץ לחומות, הפך אוטונומי בתוכם, כמעט אדונים למעשיהם, ובמקרים רבים הרבה יותר חופשיים מאשר רב אחר של התושבים והנושאים של אירופה שחיו לחסדים המלאים של הדוג'ה, נסיך, אפיפיור או מלך. ב ונציה, זה Hazzer (מילה עברית להגדיר את הגדר), הגטו - אמץ כמודל שלילי ברחבי אירופה כמציאות ולטווח פיזית - הפך בהדרגה לתוך מוסד עצמאי, "מגן" כפי שכותב ריקרדו Calimani " אשר, למרות חוסר הביטחון אז משתולל ולמרות הכל, הציע סמכויות והרשאות שאפשרו לו להישמע ולקיים מו"מ עם הרשויות חיצוניות, עם חופש היוזמה כי הוא בחלק מהמקרים מפתיעים ".
בתוך קוסמופוליטן - הגטו היה ביתם של יהודים גרמנים ואיטלקים, לבנטיני, מערב ויהודים פורטוגזיים - ולכן היה גם מרחב חדיר מאוד, באינטראקציה מתמדת עם העולם החיצון, ב primis עם העיר ונציה, עצמו רב לאומי באופן יוצא דופן גזעי, או על ידי שכנוע או פרגמטיזם.
התערוכה בבית של ארמון הדוג'ה, אשר לוקח אותנו למסע מרתק בין אמנות, היסטוריה ותרבות, ובכך ממחיש את חלוקת היישובים היהודיים באירופה לאחר 1492; הקמת הגטו האמיתי הראשון בעולם; הוויכוח על מיקומו; הצמיחה שלה בעיצוב אורבני וארכיטקטוני של הרחבות רצופים (גטו נובו, וקיו ואת Novissimo); היחסים עם שאר חלקי העיר (הסדנאות ב ריאלטו, בית הקברות, חפירת Ebrei Canale degli), ושילוב מחדש של המאה העשרים.
התערוכה מדגישה את הכללים וגם את האיסורים, התעללות, סכסוכים וחילופי; הוא מתאר חברה בגטו, מורכב קהילות שונות בפולחן דתי, שפות מדוברות, הרגלי אכילה; וגם בייצור התרבותי היהודי העשיר של האזור. לצד הנרטיב של אירועי המרחב הפיזי של הגטו, התערוכה מציעה פגישה עם אישים חשובים, כמו גם חשבונות נסיעות סקירה של ספרות, מוסיקה ותיאטרון.
מחולק לעשרה חלקים נושאיות וכרונולוגית בחדרי הדירות הדוצ'ה - עוד לפני סגירת הגטו, קוסמופוליטן ונציה, הגטו קוסמופוליטית, בתי כנסת, התרבות היהודית ואת תפקידו של נשים, סחר בין המאה השבע עשרה והשמונה עשרה, נפוליאון: פתיחת שערים והטמעה, הסוחר מוונציה, איסוף, אספנים, המאה עשרים - התערוכה מלוות גם מערכות מולטימדיה מרהיבות וטכנולוגיה חדשנית, שפותחו על ידי סטודיו Azzurro.
"ונציה, היהודים ואירופה, 1516 -2016" הוא קידם ידי עיריית ונציה ועל ידי Venezia Fondazione Musei Civici di, בתמיכת "אני 500 anni del Ghetto di Venezia" הוועדה, הקהילה היהודית של ונציה איגוד הקהילות היהודיות של איטליה, עם תרומה של מחוז ונטו, שמור ונציה Inc, קרן גלדיס Krieble דלמאס, מורשת ונציאני, ניו יורק קרן דיוויד ברג, ואת הדואר אוגו Fondazione אולגה לוי. פרויקטי המולטימדיה מומשו בשיתוף ובתמיכה של ונציה di Fondazione. הקטלוג בהוצאת Marsilio Editori מציע טקסטים על ידי מגוון של מחברים.
מאמר זה פורסם באתר האינטרנט של Palazzo Ducale.
The area was defined by two gates which, as pointed out by the Senate on 29 March, 1516, would be opened in the morning to the sound of the “Marangona” (the bell in St. Mark’s belfry that established the city’s daily timetable) and closed at night at midnight by four Christian keepers, paid by the Jews and required to reside on site without their family in order to be better able to fulfil their supervisory duties. Moreover, two high walls were to have been built (but were never constructed) to enclose the area on the side of canals surrounding it, walling up all the banks on said canals. Two Council of Ten boats with guards paid by the new “castle-dwellers” would cruise along the canal around the island at night to ensure its security. On the following 1 April, the “grida” (“declaration”) was proclaimed in Rialto and from the bridges in every city district in which Jews resided.
Organised on the occasion of the fifth centenary of the creation of Venice’s Ghetto, curated by Donatella Calabi with the scientific coordination of Gabriella Belli and the contribution of a large pool of scholars, the Venice, the Jews and Europe 1516 – 2016 exhibition aims to describe the processes that led to the creation, implementation and transformation of the first “fence” for Jews in the world.
At the same time, the exhibition expands to a wider horizon, embracing the relations established with the rest of the city and with other Jewish (and other) districts in Italy and Europe, to emphasise the fruitful relations between Jews and Venice and between Jews and civil society in the different periods of their long stay in the lagoon, in the Veneto area and in Europe and the Mediterranean. The intention is to establish a greater awareness of the cultural diversity present in cosmopolitan Venice at the beginning of the sixteenth century and the mix of knowledge, skills, customs that still comprise its most important legacy.
exhibit veniceThe task has thus not only been one of surveying the special area of the three ghettos (Nuovo, Vecchio and Nuovissimo), but also one of reflection on the cultural and linguistic exchanges, the fine craftsmanship and trades that the Jewish community has shared with the Christian population and other minorities living in this extraordinarily important mercantile city. The time span considered goes beyond the fall of the Republic and the opening of the doors at the behest of Napoleon: the exhibition will also showcase the role of Jews in the age of assimilation and during the twentieth century.
Important paintings – by Bellini and Carpaccio, Foraboschi, Hayez and Poletti, Balla and Wildt to Chagall – architectural drawings of the period, volumes in very rare original editions, archival documents, liturgical objects and furniture, together with multimedia reconstructions will enable the visitor to learn about a long-term relationship that was marked also by permeability, close contacts and cultural exchange.
The project’s initial premise is that the history of the institution of the Ghetto in Venice should be studied as part of the more general picture of the Venetian Republic’s administration of national, ethnic and religious minorities living in the city, capital of a “world economy”, as the historian Fernand Braudel called it. But it also sets out to explain how these relationships gradually broadened to a much vaster geographical area and have persisted over time, adapting to political, social and cultural changes.
In the early decades of the sixteenth century the Venetian Republic implemented a deliberate strategy of welcome, simultaneously offering guarantees and surveillance, which was more or less rigid with respect to the various national and religious communities; this welcome was extended to those communities that were important for the republic’s economic activities, such as North Europeans (with the Fondaco dei Tedeschi), the Orthodox Greeks (with a concession to build a church and a college at their expense) and, over the years, Albanians, Persians and Turks.
The Jews, like the other minorities, were “precious” for the Serenissima (as we read in some documents): its judiciary, some nobles, Doge Leonardo Loredan himself, who was “Prince” at the time of the founding decree (29 March, 1516), were well aware of this. Nevertheless, Venice, which had permitted the Jews in their territory to enter the city as war refugees – at at time when Europe was expelling them from Spain (1492) and Portugal (1496) – in the wake of the dramatic consequences of the league of Cambrai and the defeat of Agnadello, soon posed itself the question of how to treat the Jewish minority.
“At stake was the defence of fundamental cultural values for their perception of themselves. Namely”, according to Robert Bonfil, “all those values that “the myth of Venice” deemed to be most essential of all: justice, freedom and prosperity, all rooted in good governance and not least in the defence of Christian ethics, without which neither justice nor prosperity were conceivable”.
The decision not to expel the Jews but to keep them inside the ghetto was seen as the lesser evil and their enclosure, in itself an overt discrimination, ended up also becoming a useful defence, because the Jews, a politically weak entity outside the walls, became autonomous within them, almost masters of their own actions, and in many cases far freer than many other of Europe’s inhabitants and subjects who lived at the complete mercy of a doge, prince, pope or king. In Venice, this Hazzer (a Hebrew word to define the fence), the Ghetto – adopted as a negative model throughout Europe as a physical reality and term – was gradually transformed into an independent institution, “a shield” as writes Riccardo Calimani, “which, despite the then rampant insecurity and despite all, offered powers and privileges that allowed it to be heard and to negotiate with the authorities outside, with a freedom of initiative that is in some cases surprising”.
Cosmopolitan within – the Ghetto was home to German and Italian Jews, Levantine, Western and Portuguese Jews – it was therefore also a highly permeable space, in constant interaction with the outside world and, in primis with the city of Venice, itself extraordinarily multinational and multiethnic, either by conviction or pragmatism.
The exhibition at the Doge’s Palace, which takes us on a fascinating journey through art, history and culture, thus illustrates the distribution of Jewish settlements in Europe after 1492; the establishment of the first real ghetto in the world; the debate about its location; its growth and the urban and architectural shaping of successive expansions (the Ghetto Novo, the Vecchio and the Novissimo); relations with the rest of the city (the workshops at Rialto, the cemetery, the excavation of the Canale degli Ebrei), twentieth-century reintegration.
The exhibition highlights the rules and also the prohibitions, abuse, conflicts and exchanges; it describes society in the Ghetto, made up of communities differing in religious ritual, languages spoken, eating habits; and also the rich Jewish cultural production of the area. Alongside the narrative of the events marking the physical space of the Ghetto, the exhibition offers a meeting with important figures, as well as travel accounts and an overview of literature, music and theatre.
Divided into ten thematic and chronological sections in the rooms of the Doge’s apartments – Before the Ghetto, Cosmopolitan Venice, The cosmopolitan Ghetto, Synagogues, Jewish culture and the role of women, Trade between the seventeenth and eighteenth century, Napoleon: the opening of the gates and assimilation, The merchant of Venice, Collecting, collectors, the twentieth century – the exhibition is also accompanied by breathtaking multimedia systems and innovative technology, developed by Studio Azzurro.
“Venice, the Jews and Europe, 1516 -2016” is promoted by the City of Venice and by the Fondazione Musei Civici di Venezia, with the support of “I 500 anni del Ghetto di Venezia” Committee, the Jewish Community of Venice and the Union of Italian Jewish Communities, with the contribution of the Veneto Region, Save Venice Inc, the Gladys Krieble Delmas Foundation, Venetian Heritage, the David Berg Foundation New York, and the Fondazione Ugo e Olga Levi. The multimedia projects been realised in cooperation and with the support of the Fondazione di Venezia. The catalogue published by Marsilio Editori offers texts by a variety of authors.
This article has been published in the website of Palazzo Ducale.